Table of Contents
ToggleIf you are thinking of getting pregnant, you must have heard that females should try while they are ovulating. There must be many questions in mind regarding: What is ovulation? How is pregnancy connected to it? What are the symptoms of ovulation? Ovulation is a process that every woman goes through once a month. It is a phase in the menstrual cycle where the ovary releases a mature egg.
A female can only get pregnant when she has sex during the five days before ovulation or on the day of ovulation. A female opting for an IVF treatment must record her ovulation period. Sometime after ovulation, the fertility clinic may have you start taking a GnRH antagonist or a GnRH agonist so that the doctor can have complete control over the ovulation cycle. There are several signs of ovulation that can indicate your ovulation cycle. In this blog, we will cover all your dilemmas about ovulation in depth.

What is Ovulation?
Ovulation is a process that occurs when the ovary releases a mature egg. After its release, the egg moves down the fallopian tube and stays there for 12 to 24 hours to get fertilized. It usually occurs mid-cycle, around two weeks or so before menstruation starts.
Tight regulation and controlled changes between the following hormones are crucial for developing and releasing an oocyte into the adnexal uterine structures. The fluctuation between the following hormones regulates ovulation.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH): GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and released by the hypothalamus. Variations in GnRH pulse frequency stimulate the release of FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary gland. Low-frequency GnRH pulses are liable for FSH secretion, whereas high-frequency pulses are liable for LH secretion.
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): FSH is synthesized by gonadotropin and secreted from the anterior pituitary gland in retort to slow-frequency pulsatile GnRH. It stimulates the growth and maturation of immature oocytes into mature secondary follicles before ovulation.
- Estrogen: It is a steroid hormone responsible for the growth and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH): LH is a gonadotropin synthesized and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland in response to high-frequency GnRH release. It induces ovulation, prepares for fertilized oocyte uterine implantation, and the ovarian production of progesterone through stimulation of theca cells and luteinized granulosa cells.
- Progesterone: Progesterone is a steroid hormone accountable for preparing the endometrium for the uterine implantation of the fertilized egg and maintenance of pregnancy.
There are four phases of the menstrual cycle: menstruation, the follicular phase, ovulation, the luteal phase. In the ovulation phase, the developing follicle causes a rise in estrogen level during the follicular phase. These rising levels are recognized by the hypothalamus in the brain, and it releases a chemical called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). GnRH hormone stimulates the pituitary gland to cause a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) and FSH levels. High levels of LH trigger ovulation within two days. The egg is funneled into the fallopian tube and toward the uterus by waves of tiny, hair-like projections. The egg typically lives for only around 24 hours. If it does not encounter a sperm during this time, it will die.
Determining the ovulation time is important when a female is going through an IVF treatment as it helps the doctors to prepare the injections to take by the patient during IVF Treatment.
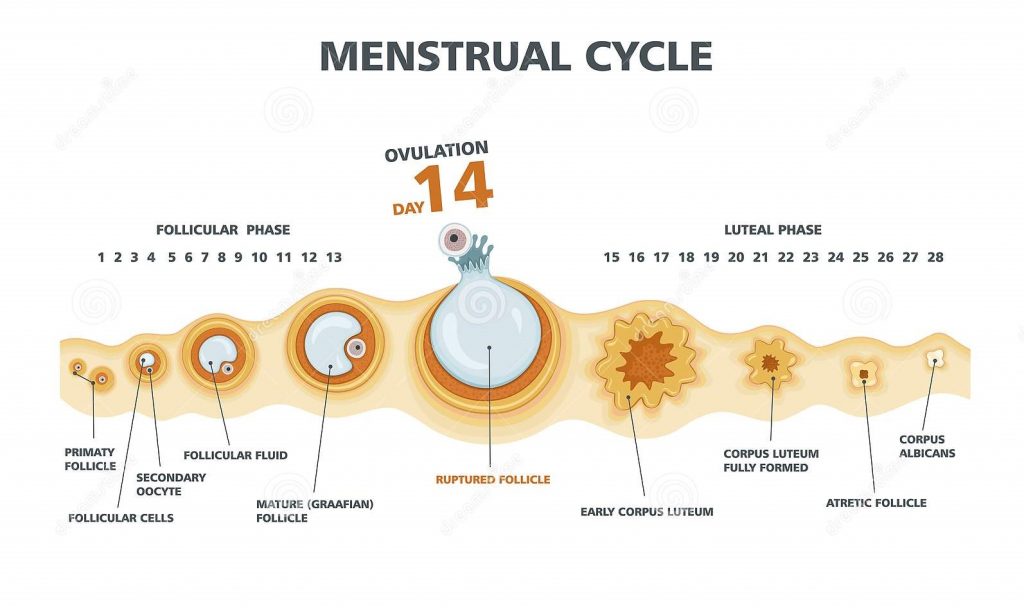
When Do Females Ovulate?
In the case of a typical 28-day menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs about 14 days before the start of the next menstrual period. However, each person’s cycle length may differ, and the time between ovulation and the next menstrual period may vary. For some women, ovulation does not always occur or can be irregular. In general, you will not ovulate if you’re pregnant, take birth control pills consistently and on time, or have gone through menopause.
The ovulation cycle of a woman may also be irregular because of certain disorders such as polycystic ovary syndrome or premature ovarian failures and certain medications such as some antidepressants, anti-nausea medications, and chemotherapy. Many other lifestyle factors such as stress or being significantly underweight or overweight may also affect menstruation and ovulation. Suppose you’re dealing with irregular, short (fewer than 21 days), or long (more than 35 days) menstrual cycles. In that case, you should consult a physician to rule out any medical conditions that might be inducing those irregular cycles.
A woman does not ovulate while breastfeeding, but there are always exceptions, so you can not depend on breastfeeding as a means of birth control. Tracking ovulation if you do not have a regular 28-day menstrual cycle like many women can indeed be more difficult, but keep in mind that ovulation occurs 14 days before the onset of menstruation. Thus, you can determine the length of your cycle by keeping a menstrual calendar.
Once the surface of the ovary releases the mature egg, sperm can potentially fertilize it for about 24 hours. You do not have to have sex on the exact day of ovulation to get pregnant. There is a six-day fertile window in your cycle—the five days leading up to ovulation and the day you ovulate. Of those six days, you’re most fertile during the two to three days before ovulation and the day of ovulation itself. The egg will die within 12 to 24 hours after ovulation, and you typically can not get pregnant until your next menstrual cycle. If you’re not trying to conceive, though, you should still use birth control at all times as a precaution.
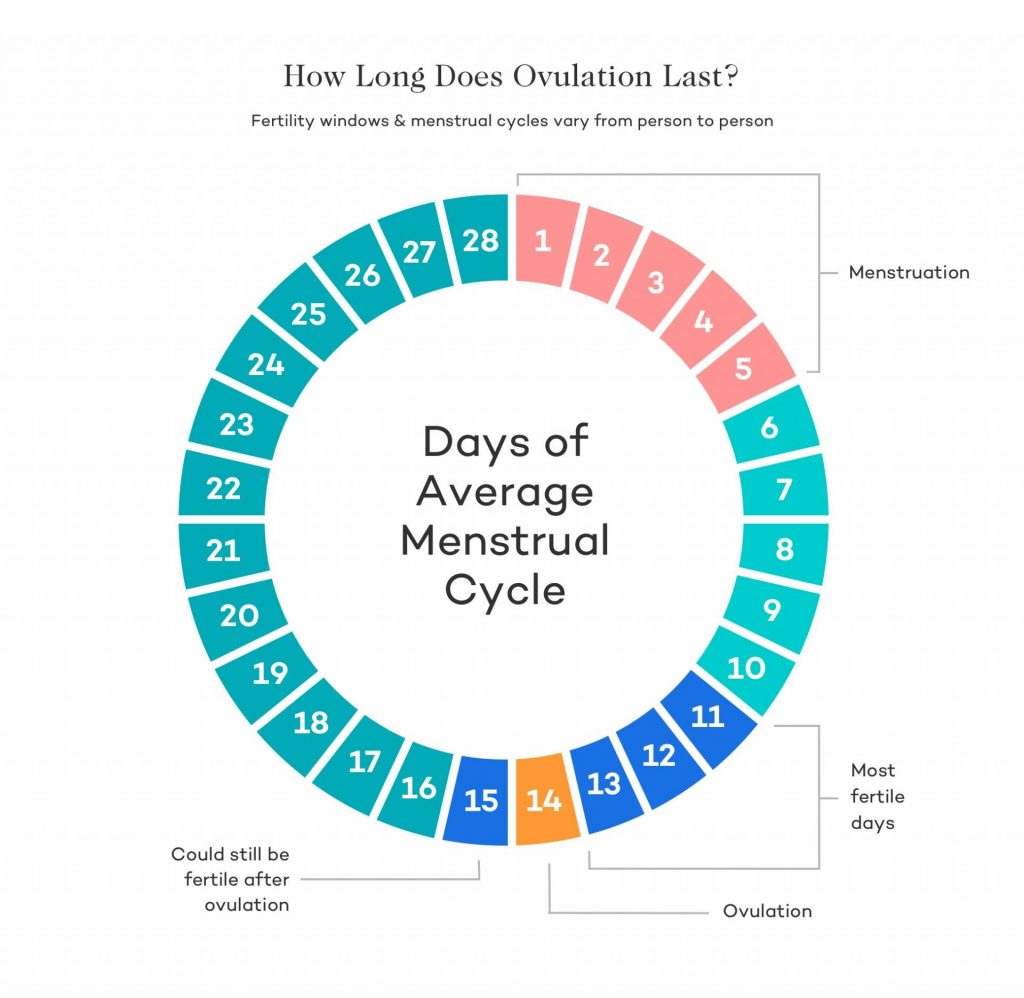
Ovulation Symptoms To Help You Conceive Naturally
There are many symptoms of ovulation that will help you identify whether you’re ovulating. Before and during ovulation, hormonal shifts may affect the entire body, prompting ovulation symptoms. Although the symptoms differ for every woman, some common ovulation signs are:
Cervical mucus changes
When you are near ovulation, your body produces more estrogen, which causes the cervical mucus to become clear and stretchy, like egg white.
Heightened senses
In the case of some women, they develop a more acute sense of smell and taste in the latter half of regular menstruation. In this phase, your body is on prime to attract the male pheromone androstenone.
Breast soreness or tenderness
Another in the series of ovulation signs is tender breasts or sore nipples. Some women experience this tenderness just before ovulation, while others may feel it right after ovulation occurs.
Mild pelvic or lower abdominal pain
Some women feel a mild ache or pain in the lower abdomen, usually on either side. This side effect can last between a few minutes and a few hours. You might also undergo light vaginal bleeding, nausea, discharge, along with mild pain.
Light spotting or discharge
Brown discharge or spotting is not a very common symptom but normal during ovulation. The discharge may range from red to dark brown. If the spotting persists, you should see a physician to check for any infection and the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy.
Additionally, Check Out: How to Stop Brown Discharge During Pregnancy?
Libido changes
Another common ovulation symptom is a change in overall sexual drive. Some women experienced that their sex drive increased during ovulation.
Changes in the cervix
Your cervix may become higher, softer, and more open during ovulation. Many women with a regular cycle feel their cervix is softer, like touching your lips right before ovulation, but after ovulation, it will feel harder, more like touching the tip of your nose.
Nausea and headaches
During ovulation, you may feel nausea and headaches due to the change in your estrogen and progesterone levels.
Changes in your basal body temperature
Your basal body temperature will rise during ovulation and stay elevated during that time.
Mild Bloating
Your body experiences several hormonal changes during ovulation. Just before ovulation begins, levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and estrogen spike, which can lead to bloating.
How To Predict Ovulation Without Experts
In case you want to get pregnant or merely just want to know when you’re ovulating. There are various methods to predict your ovulation you can use.
Basal body temperature monitoring: To predict your ovulation, you should keep track of your basal body temperature over a series of months. BBT is your body’s temperature at rest. Basal body temperature remains relatively consistent at the beginning of your cycle. As you get nearer to ovulation, you will see a slight dip in basal body temperature, which is then followed by an increase, typically about 0.4 to 1.0 degrees, just after ovulation.
Menstrual charting: Another way to track ovulation is to record the days your period begins and ends for several months. You will likely be regularly ovulating if you have regular menstrual cycles between 25 and 35 days, with ovulation occurring about 14 days before menstruation.
Ovulation kit: OTC ovulation predictor kits are also a way to track your cycle, but they are a bit more expensive than others. OTC measures your luteinizing hormone (LH) levels, which can be detected in your urine. You have to pee on the stick and wait for a line to appear. If the line’s color matches the shade shown on the instructions, ovulation is imminent within 24 to 48 hours.
Fertility monitor: A fertility monitor is used to identify the five most fertile days. The monitor estimates LH and estrogen levels to determine your two peak fertile days and the one to five fertile days guiding up to them. They are more expensive than ovulation kits.

Medical Tests for Ovulation
If you have doubts that you’re not ovulating regularly or ovulating at all, then you must consult a doctor because you might be having a fertility problem. Some causes of infertility get worse with time, so it is better to get it checked on time.
Your doctor will determine whether you’re ovulating or not by a progesterone blood test. The hormone progesterone rises after ovulation, and in the case of no ovulation, your progesterone results will be abnormally low. Doctors usually do this test on day 21 of your cycle.
Doctors might run some other blood tests to determine why you’re not ovulating. They will also test your FSH and AMH levels, along with estrogen, prolactin, androgens, and thyroid hormones. Your doctor may also ask for a transvaginal ultrasound, which will enable the doctor to see if follicles are developing in the ovary. After ovulation, ultrasound can detect whether a follicle broke open and released an egg.
Also If your bloating lasts for a long time, it could be because of medical conditions like PCOS, endometriosis, or an ovarian cyst. If you have severe prolonged abdominal pain or abnormal bleeding, it could also be because of UTI, endometriosis, and other infections. In this situation, schedule a checkup with your doctor to rule out these possibilities.
Aastha Fertility Will Take Care of Your Pregnancy-Related Things
If you’re trying to conceive and looking for the best fertility center in Jaipur, then the Aastha fertility center is the finest among all the centers. Aastha fertility has the best IVF Specialists, They take care of your pregnancy, starting from ovulation to delivery. They have the best medical staff and the highest success rate for treatment like Intrauterine Insemination (IUI), In-Vitro Fertilizations, and IVF With PGS. If you’re having any trouble conceiving, you can consult our experienced fertility team. We will help you get pregnant with the most suitable method for you and will make your pregnancy journey smooth.
Conclusion
Some persons have ovulation symptoms and indicators. These include bloating, mildly raised body temperature, breast soreness, cervical mucus and saliva changes, and abdominal ache or cramps. If you’re trying to get pregnant, you should track your ovulation cycle, as it can be helpful in understanding when to have sex for better results. Your fertile window begins with ovulation. However, pregnancy can occur up to 5 days before and one day after that. If you have difficulty conceiving, you can visit fertility clinics and join support groups.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are some tips for increasing my chances of getting pregnant?
You could elevate the chances of getting pregnant by exercising regularly, ceasing alcohol, tracking your ovulation cycle to know when to have sex more, reducing caffeine intake, and avoiding smoking.
2. Pregnancy’s early warning signs and symptoms?
Pregnancy’s early signs and symptoms include breast tenderness, missed periods, morning sickness, increased urination, mood swings, fatigue, and mild abdominal cramps.
3. When should you take a pregnancy test?
Take a pregnancy test after a day of missing your period.
4. Can stress or other factors affect ovulation and cause symptoms to change?
Yes, An extremely high or low body weight, a recent significant weight gain or loss, or excessive physical or emotional stress can all interfere with the production of hormones and impair ovulation.





Leave a comment