Table of Contents
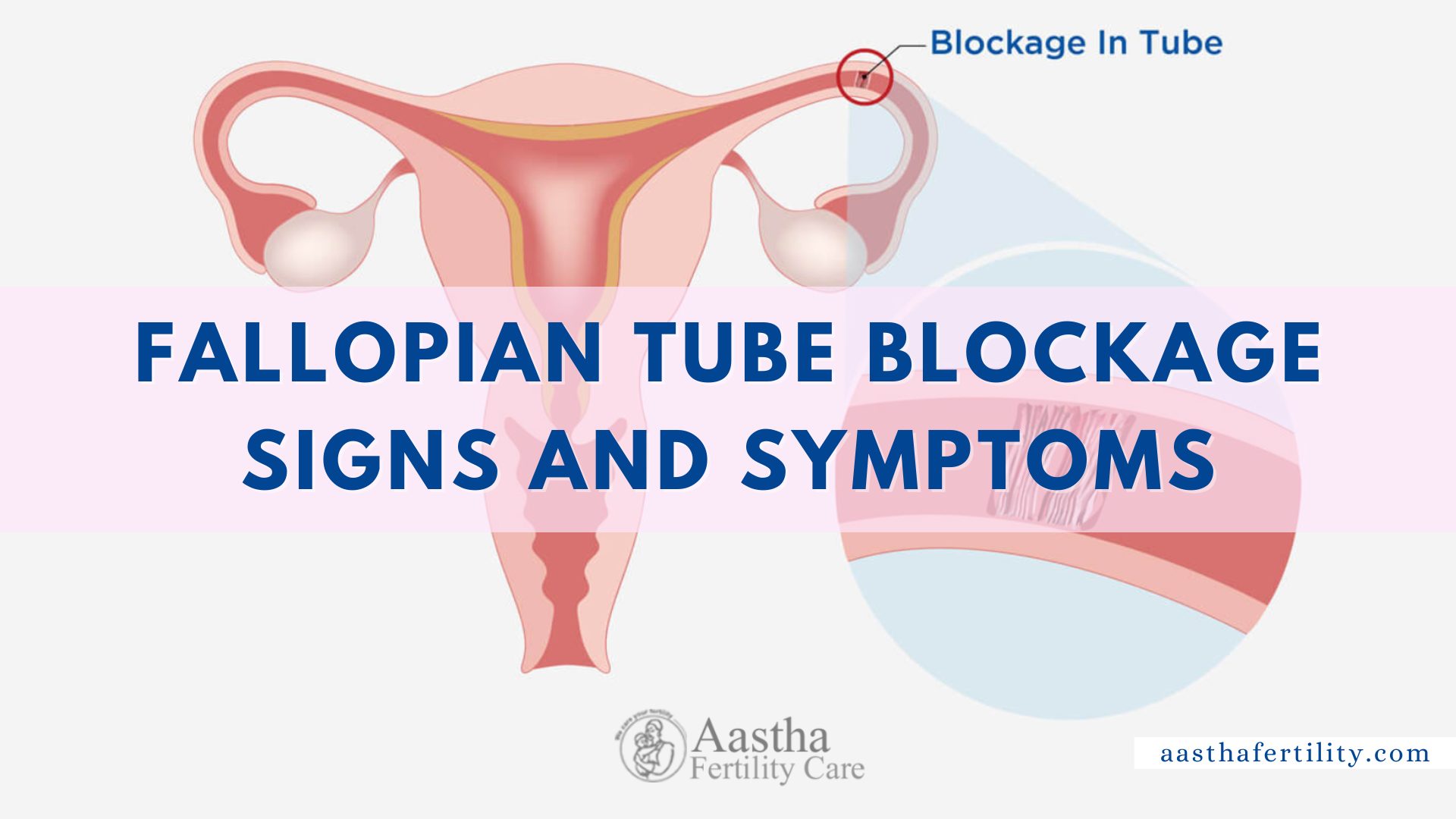
ToggleThe fallopian tubes or uterine tubes are bilateral tubes between the ovaries and the uterus in the female pelvis. They act as channels for oocyte transport and fertilization. Given this role, the fallopian tubes are a common cause of infertility and the target of intended surgical sterilization. They can also be spots of ascending infection or neoplasms. It also helps lead the mature egg from the ovaries to the uterus. Still, in a few women, an obstruction prevents the egg from traveling down the tube, causing a blocked fallopian tube, also known as tubal factor infertility. It is the reason behind infertility in up to 30% of infertile women.
Functions Of Fallopian Tube
The prime fallopian tube function is to carry eggs from the ovary to the uterus. The fimbriae pick up the eggs and then sweep them towards the uterus. This movement is influenced by the beating of the cilia and by peristalsis, which is the rhythmic contraction of the muscles of the tubes.
The fertilization generally ensues in the fallopian tubes. The sperm move out from the uterus into the conduits, where they may meet and fertilize an egg. The fertilized egg then resumes its journey toward the uterus. If a fertilized egg implants in the uterus and persists in developing can cause uterine pregnancy.
Successful eggs travel through the fallopian tubes is necessary for a woman to get pregnant without medical intervention.
Symptoms Of Blocked Fallopian Tube
Blocked fallopian tubes rarely show symptoms, unlike anovulation, where irregular menstrual cycles may indicate a problem. The first blocked fallopian tube symptom is often infertility. If a woman doesn’t get pregnant after one year of trying, the doctor will order a specialized X-ray to check her fallopian tubes and another basic fertility testing.
Women with hydrosalpinx might experience lower abdominal pain and unusual vaginal discharge, but not every woman will have these symptoms. Hydrosalpinx is when a blockage causes the tube to dilate and fill with fluid.
In some cases, the causes of blocked fallopian tubes may also cause symptoms. For instance, endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) may cause painful menstruation and painful sexual intercourse.
Symptoms that could indicate pelvic infection include:
- general pelvic pain
- nausea and vomiting (in acute cases)
- pain during sexual intercourse
- fever over 101 (in acute cases)
- foul-smelling vaginal discharge
- severe lower abdominal or pelvic pain (in acute cases)
Acute pelvic infections can be life-threatening. If you have a high fever or acute pain, contact your doctor immediately.
Causes Of Blocked Fallopian Tube
Several conditions damage or block the fallopian tube, including:
- Pelvic infections
- Use of an intrauterine device if it causes a pelvic infection which happens in rare cases
- Endometriosis
- A ruptured appendix
- Surgery in the pelvis or lower abdomen
- Inflammation such as that caused by tuberculosis damages the uterus and fallopian tubes
- A mislocated pregnancy in the fallopian tubes
Pelvic inflammatory disease, resulting from bacterial infections, can affect the fallopian tubes and surrounding reproductive tissue. The bacteria that cause these infections are often transmitted during sexual intercourse with a partner who has a sexually transmitted infection (STI). If an infection occurs in the cervix, it may spread upward to the uterus and sometimes the fallopian tubes. Some STIs, such as chlamydia, can infect the fallopian tubes without causing any symptoms. These untreated infections may permanently damage the fallopian tubes and surrounding tissue. Scar tissue might form and block the fallopian tubes.
Pelvic abnormalities can block the fallopian tubes or prevent a fertilized egg from implanting in the uterus. They include the following:
- Congenital disabilities of the uterus and fallopian tubes
- Endometriosis
- Bands of scar tissue that form between usually unconnected structures in the uterus or pelvis
- Fibroids or polyps in the uterus
Infections or injuries usually cause adhesions in the uterus during surgery, dilation, and curettage (D and C). This disorder is called Asherman syndrome.
Diagnosis
the following methods are used to diagnose the problems with the fallopian tube:
- Hysterosalpingography or sonohysterography
- Sometimes a blood test to review for antibodies to chlamydiae
- Laparoscopy or hysteroscopy
Doctors ask for these procedures to determine whether the fallopian tubes are blocked. Diagnostics and treatments are usually carried out simultaneously during laparoscopy and hysteroscopy.
Hysterosalpingography
The most common application of hysterosalpingography is to inspect for problems with the fallopian tubes.
After injecting a radiopaque contrast agent through the cervix, medical representatives take X-rays. A contrast agent is administered a few days after a woman’s menstrual period has ended. This helps outline the interior of the uterus and fallopian tubes so that a physician can determine if there are any abnormalities. Hysterosalpingography is a procedure that uses an x-ray to detect structural disorders that can block the fallopian tubes and has a 15% false-positive rate. Fertility in young women occurs to be slightly improved after normal results, possibly because the procedure temporarily widens (dilates) the conduits or clears the tubes of mucus and debris. Before doing any additional tests on fallopian tube function, doctors may wait to see if young women become pregnant after this procedure.
Sonohysterography
Sonohysterography is sometimes used to catch and assess further issues with the fallopian tubes and other abnormalities in the pelvis.
Saline is injected into the uterus during ultrasound imaging so that the uterus will appear enlarged on the monitor. If the solution flows into the fallopian tubes, they are not blocked. Sonohysterography can be performed quickly and does not require an anesthetic. It is known to be safer than hysterosalpingography because it does not require radiation or injection of a dye. However, its accuracy depends on how skilled the practitioner doing the test is.
Laparoscopy
In case the fallopian tubes are blocked or a woman may have endometriosis, a tiny viewing conduit called a laparoscope is inserted in the pelvic cavity via a small incision just below the navel. Usually, they give a general anesthetic. Laparoscopy enables doctors to view the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries directly. However, it is rare for a doctor to prescribe this procedure.
By inserting instruments through the laparoscope, abnormal tissue within the pelvis may also be dislodged or removed.
Hysteroscopy
If a uterine abnormality is detected, doctors examine the uterus with a viewing conduit called a hysteroscope inserted via the vagina and cervix of the uterus. Suppose adhesions, a polyp, or a small fibroid is detected. In that case, instruments inserted through the hysteroscope may come handy to dislodge or remove the abnormal tissue, increasing the woman’s chances of becoming pregnant.
Blood Tests
Sometimes doctors might ask to perform some blood tests to check for antibodies to chlamydiae. The existence of antibodies implies past infection with chlamydiae, resulting in infertility.
Complications of Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Ectopic pregnancy is the most prevalent complication of blocked fallopian tubes and treatment. A partially blocked fallopian tube may allow the fertilization of an egg. Still, it may get stuck in the conduit, resulting in an ectopic pregnancy.
An ectopic pregnancy can also result from surgery that removes part of the fallopian tube. Because of the risks associated with surgery, doctors often recommend IVF for otherwise healthy women with blocked fallopian tubes.
Conclusion
Problems in the fallopian tube can cause infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Though many treatments are available to treat the blockage, the treatment might also result in ectopic pregnancy. To eradicate the risk of ectopic pregnancy, infertility specialists suggest IVF. Aastha Fertility Care is the most reliable and successful IVF center. They provide you with the best advice and treatment that would make your pregnancy journey smooth.


Leave a comment