Table of Contents
ToggleThere are several things about pregnancy and thyroid that are prevailing in today’s world. Some may hear that the thyroid can complicate pregnancy, while many women believe pregnancy with the thyroid often results in miscarriages. However, at Aastha Fertility Care, we will help you navigate all the complications and help you with a healthy pregnancy even with thyroid.
Optimum levels of Thyroid hormones are essential for optimal fetal growth during the first trimester months of pregnancy. It is common for pregnant women to have a hormonal imbalance and lead to hypothyroidism (lower level of Thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (higher level of Thyroid), hence regular check on thyroid levels is a must during the entire journey from conceiving to delivering the baby.
Before we discuss our treatments for Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism we want our reader to understand what is thyroid, its types and symptoms and how Thyroid and pregnancy are related.
What Is Thyroid?
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. Whereas a gland is an organ that produces hormones that aid in the functioning of your body. The thyroid gland produces hormones (chemicals) critical for your health mainly having an impact on your heart rate (the pace at which your heart beats) and metabolism.
The thyroid gland sometimes produces excessive or insufficient amounts of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) hormones leading to thyroid condition which may be one of the possible reasons for female infertility.
Certain women develop a thyroid problem before pregnancy, and others may have their first thyroid difficulties during pregnancy or shortly after giving birth.
With proper care, a woman can avoid any pregnancy and thyroid complications. A healthy pregnancy with thyroid medication and monitoring thyroid levels throughout the pregnancy will keep you and your baby healthy. However, untreated thyroid disorders may pose difficulties for you and the baby during and post-pregnancy.
Pregnancy & Thyroid Hormones: Role Of Thyroid Hormones In Pregnancy
Thyroid hormones are necessary for your baby’s nervous system and brain to grow normally. Within the first trimester—the first three months of getting pregnant, the womb entirely depends on your levels of thyroid hormone, delivered via the placenta. About 12 weeks of pregnancy, your baby’s thyroid begins to function independently but does not produce adequate thyroid hormone till the 18 to 20th weeks of pregnancy.
Thyroid hormone concentrations in your blood elevate by two pregnancy-related hormones: human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and estrogen. The thyroid gland grows somewhat during pregnancy in healthy women. However, it is not enough for a doctor to detect during a medical examination.
Thyroid problems may be difficult to identify during pregnancy due to unawareness and carelessness towards symptoms associated with pregnancy and thyroid abnormalities. Well, specific signs of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism are more noticeable, and when examined may prompt your physician to conduct thyroid tests.
Another kind of thyroid condition, postpartum thyroiditis, may develop even after your child’s birth.
So, Thyroid and pregnancy relations can be complicated even after your delivery.
Types Of Thyroid
During pregnancy, thyroid symptoms differ as per the type of thyroid. You need to understand how the thyroid affects pregnancy in order to get the treatment and respond to the treatment.
So, there are two significant kinds of thyroid problems:
1. Hyperthyroidism (“hyper” indicates excessive):
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid is hyperactive and produces an excessive thyroid hormone. Further, numerous bodily activities may become accelerated due to this illness. During pregnancy, hyperthyroidism is often due to Graves’ disease’s autoimmune condition.
Autoimmune disorders are a group of diseases that occur when antibodies (body cells that combat infection) mistakenly target healthy tissue. When someone has Graves’ disease, their immune system produces antibodies that cause their thyroid to produce an abnormal amount of thyroid hormone.
Symptoms:
Specific symptoms of hyperthyroidism commonly occur throughout normal pregnancies, including an increased heart rate, difficulty coping with the heat, and fatigue.
Other indications and symptoms of hyperthyroidism include the following:
- rapid and erratic pulse
- shaky hands
- unexplained weight loss or inability to have the ideal pregnancy weight
In such cases, the pregnancy and thyroid can affect your baby if left untreated. The complications include:
- preterm birth
- miscarriage
- low birth weight
- Preeclampsia—a potentially fatal increase in blood pressure during late pregnancy
- thyroid storm—an abrupt, rapid worsening of symptoms
2. Hypothyroidism (“hypo” implies insufficient or insufficient)
Hypothyroidism occurs whenever the thyroid is underactive and does not produce enough thyroid hormones, slowing day to day body activities. Hypothyroidism occurs most often during pregnancy due to Hashimoto’s autoimmune illness.
Further, when someone has Hashimoto’s disease, their immune system produces antibodies that target and destroy their thyroid, preventing them from producing thyroid hormones.
The pregnancy thyroid symptoms in such cases are:
The indications of underactive thyroid are the same in pregnant women and other individuals with hypothyroidism. Symptoms include the following:
- excessive exhaustion
- unable to cope with cold
- muscular cramps
- severe constipation memory or concentration difficulties
- Excessive weight gain
Most hypothyroidism instances during pregnancy are mild and may present with no symptoms.
If during pregnancy, the hypothyroidism doesn’t receive treatment, it can lead to:
- Preeclampsia—a potentially severe increase in blood pressure during late pregnancy
- Anaemia
- Congestive heart failure occurs rarely
- Miscarriage
- Low birth weight
- Stillbirth
Pregnancy and thyroid complications like miscarriages occur in the case of hypothyroidism.
So, this is how the thyroid affects pregnancy. Additionally, pregnancy for thyroid patients is possible in both cases if they take the right medication and the proper diet and follow the doctor’s instructions.
Treatment To Avoid Thyroid Pregnancy Complications
To avoid thyroid pregnancy complications, you must take the proper medication and undergo treatment for your condition.
Several medications used for treating thyroid disorders are harmless for your developing fetus. Thyroid medications may assist you in maintaining an optimal amount of thyroid hormones in your body. Throughout pregnancy, your doctor will do blood tests to determine your TSH and T4 levels and ensure that your medication is administered appropriately (dose).
Your provider may choose to modify or replace your prescription to ensure that it is safe for your infant. If you are currently on thyroid medication during pregnancy, continue taking it and see your doctor immediately.
Further, pregnancy with thyroid medication is entirely safe and is necessary for a healthy pregnancy.
Treatment For Hyperthyroidism
You will certainly not need medication if you have moderate hyperthyroidism during pregnancy. If hyperthyroidism is associated with hyperemesis gravidarum, treatment is mainly for vomiting and dehydration.
If you have severe hyperthyroidism, the doctor may give antithyroid medications. So this forces your thyroid gland to produce less thyroid hormone, and this medicine keeps an excessive thyroid hormone out of your baby’s system.
You could choose to see a professional, like an endocrinologist or a specialist in maternal-fetal medicine, who can closely monitor your baby to ensure that you receive the correct amount.
Treatment For Hypothyroidism
Levothyroxine is the most often prescribed medication for hypothyroidism during pregnancy and thyroid. Levothyroxine is used to replace the T4 thyroid hormone that your thyroid does not produce or produces insufficiently.
Further, pregnancy is not a safe time to use thyroid medications that include the T3 hormone.
If you had hypothyroidism previously becoming pregnant, you would almost certainly need to elevate your medication dosage throughout pregnancy. Discuss your medication with your health care practitioner as soon as you learn you’re pregnant. Your physician can ensure you receive the correct dosage by monitoring your pregnancy time thyroid level and the TSH levels.
Pregnancy With PCOS And Thyroid
Hypothyroidism is a relatively prevalent complication of PCOS, and having a pre-existing thyroid problem might make pregnancy more difficult. It is essential to get your thyroid tested and talk with your doctor about the best approach for reestablishing normal thyroid functioning without risking your pregnancy.
Further, PCOS in females might make it increasingly challenging for the egg to be fertilized by sperm in the womb regardless of egg release. However, pregnancy with PCOS and thyroid is possible. In such circumstances, in vitro fertilization (IVF), where the egg is fertilized in a laboratory with sperm, may be the best option. After a successful IVF cycle, your doctor can proceed with pregnancy with thyroid medication. There may be chances of a healthy pregnancy.
Also Read: https://aasthafertility.com/pcod-causes-and-symptoms/
Some IVF facts include:
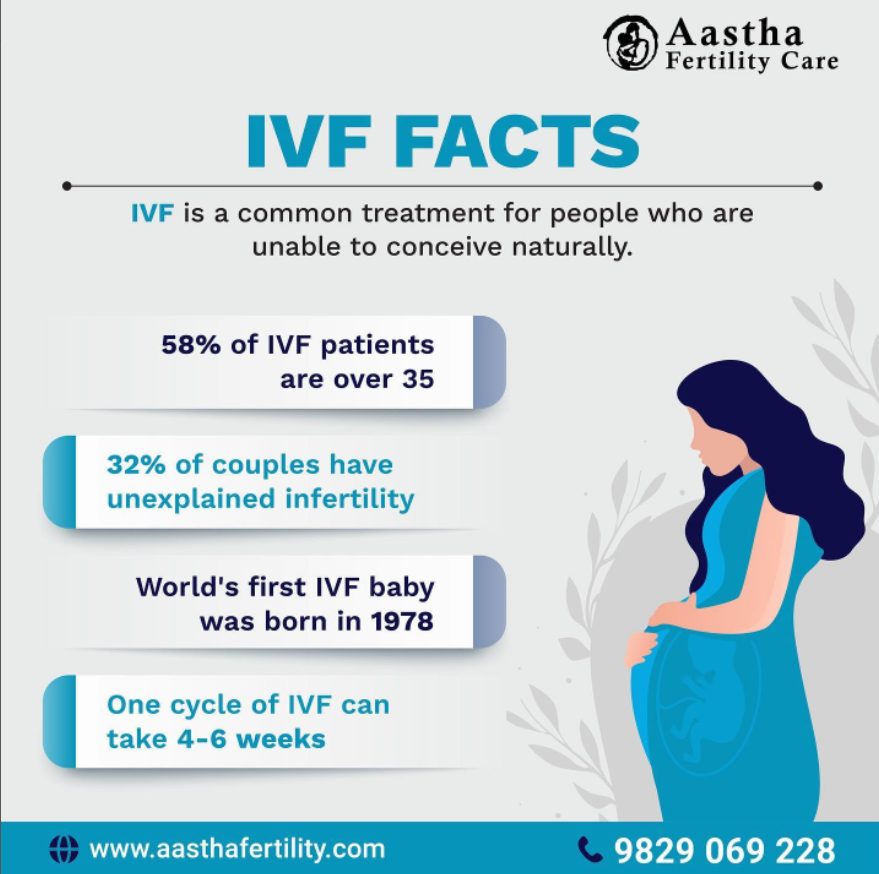
(Ref: https://www.instagram.com/p/CaroHm_g0VE/)
Conclusion
Pregnancy and thyroid are no more a complication, thanks to modern medical science, technological advancement, and the support of Aastha Fertility Care. Book your consultation today if you face pregnancy issues, and our IVF Specialists can offer personalized treatment.





Leave a comment