Table of Contents
ToggleAre you diagnosed with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or suspect you might experience it? You might be undoubtedly wondering what’s happening in your body. You can have different adverse effects or symptoms and require different treatments depending on your polycystic ovarian syndrome type.
Understanding PCOS
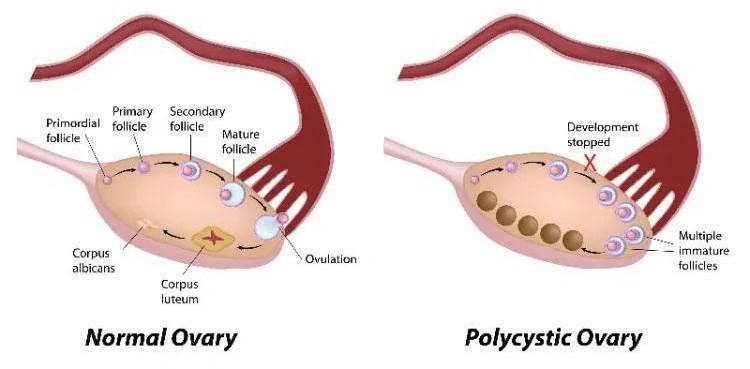
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome or PCOS problem is a prevalent condition that affects the ovaries’ function. PCOS could be why you have had fertility concerns, abundant body hair, or irregular menstrual cycle and abnormal period pain. Polycystic ovaries have tiny undeveloped sacs that form but do not release eggs. If ovulation symptoms indicate failure, there are changes in hormone levels, and Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome may cause more androgen and less progesterone, resulting in the symptoms mentioned above.
Many studies show that individuals with inflammatory PCOS are prone to experience increased CRP levels, indicating that their bodies experience a specific type of inflammation. In addition, you may also experience higher levels of other inflammation markers, such as inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress, and white blood cells known as monocytes and lymphocytes. All such factors are present during inflammation and are also included in the immune response. Besides, inflammatory PCOS type is caused due to a combination of many factors, including inflammatory foods, environmental toxins, stress, and genetics. CRP level elevations have also been linked to heart disease, insulin resistance, and diabetes, which are more frequent in inflammation PCOS symptoms.
Causes Of Inflammation In PCOS
Although the actual cause of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is unknown, there is little evidence of genetics. Instead, inflammatory PCOS causes may be several, including the following:
Higher Androgens Levels (Male Hormones)
The ovaries cannot ovulate or release eggs due to high testosterone levels, resulting in irregular menstruation periods. In addition, fluid-filled tiny sacs may form in the ovaries due to irregular ovulation. Excess hair growth and acne are also symptoms of high androgen levels in women.
Insulin Resistance
The rise in insulin levels prompts the ovaries to release and make androgens (male hormone). Consequently, increased androgens suppress ovulation and contribute to other symptoms of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Insulin regulates how the body consumes sugar or glucose for energy and process. Insulin resistance occurs when your body does not properly process insulin, resulting in elevated blood glucose levels. Although not every person with insulin resistance has diabetes or high blood sugar, insulin resistance may cause diabetes. Insulin resistance can also be caused by being obese or overweight, which is indicated by an increased insulin level, even though you have an average blood glucose level.
Low-Level Inflammation
Chronic low-grade inflammation is prevalent in individuals with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Therefore, your medical provider may measure white blood cell levels and C-reactive protein (CRP) that exhibit the inflammation level in your body.
Treating Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome

The inflammatory PCOS treatment is determined by your health concerns, medical history, and symptoms, as well as whether or not you want to conceive. Lifestyle changes and a combination of both may be used as treatment options. If you don’t want to conceive, your treatment options include the following:
Androgen-Blocking Medication
A few drugs may assist in blocking the androgens effect and control hair growth and acne caused by Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. However, you must consult your medical practitioner about considering appropriate medications.
Hormonal Contraception
All treatment options are intrauterine devices (IUD), vaginal rings, shots, patches, and birth control pills. Hormonal birth control assists in reducing excess hair growth, improving acne, and regulating your menstrual cycle.
Insulin-Responsive Medication
Metformin drugs assist your body’s insulin processing. A few patients with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) notice changes in their menstrual cycles when their insulin levels are under control.
Lifestyle Changes
A good diet chart for PCOS is helpful for losing weight and may positively affect your insulin levels.
Besides, if you want to conceive in the future or at present, your treatment options for Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) include the following:
Drugs to Release an Egg or Ovulation
Ovulation is the first step in a successful conception. In women with PCOS, certain medicines have been shown to induce ovulation. For example, gonadotropins are administered through injection, while letrozole and Clomiphene are oral.
Surgery
Ovarian drilling is a surgical procedure that removes tissues in the ovaries that produce androgen hormones, promoting ovulation. However, surgeons are now less likely to undertake this surgery due to the advent of advanced drugs.
In-Vitro Fertilization
In a laboratory, your egg is fertilized with your partner’s sperm before getting transferred to the uterus. If medicine doesn’t assist with ovulation, IVF treatment is an alternative for female infertility with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome to get a successful test tube baby.
Health Risks Associated With Inflammatory Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Inflammation in PCOS has been associated with an increased risk of various health problems, including the following:
- Anxiety and depression
- Cardiovascular disease
- Diabetes
- Endometrial cancer
- Endometrial hyperplasia
- High blood pressure
- Sleep disorders, including sleep apnea
You must understand the risks of getting health disorders by speaking with your healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) may disappear due to the hormonal changes brought on by menopause, although this is not always the case. Hormone imbalances often can persist until menopause, indicating that your imbalance does not alter as you become older. Suppose your symptoms are bothering you or affecting your quality of life. In that case, you must book an appointment at Aastha Fertility Care and speak to your healthcare professional about treatment options since your body might be experiencing inflammatory PCOS.





Leave a comment